In recent years, Vietnam’s economy has maintained relatively fast growth. In 2021, the country’s economy achieved 2.58% growth, with a GDP of $362.619 billion. Vietnam is basically politically stable and its economy is growing at an average annual rate of over 7%. For many years in a row, China has been Vietnam’s largest trading partner, largest import market and second largest export market, playing a pivotal role in Vietnam’s foreign trade. According to statistics from Vietnam’s Ministry of Planning and Investment, as of October 2021, China had invested in 3,296 projects in Vietnam with a total agreement value of US $20.96 billion, ranking seventh among countries and regions that have invested in Vietnam. The investment mainly focuses on the processing and manufacturing industries, especially the electronics, mobile phones, computers, textiles and clothing, machinery and equipment and other industries.
Textile Industry condition
In 2020, Vietnam overtook Bangladesh to become the world’s second largest exporter of textiles and clothing. In 2021, the output value of Vietnam’s textile industry was $52 billion, and the total export value was $39 billion, up by 11.2% year-on-year. About 2m people are employed in the country’s textile industry. In 2021, Vietnam’s textile and apparel market share has risen to the second place in the world, accounting for about 5.1%. At present, Vietnam has about 9.5 million spindle and about 150,000 head of air spinning. Foreign-owned companies account for about 60% of the country’s total, with the private sector outnumbering the state by about 3:1.
The production capacity of Vietnam’s textile industry is mainly distributed in the south, central and north regions, with Ho Chi Minh City as the center in the south, radiating to the surrounding provinces. The central region, where Da Nang and Hue are located, accounts for about 10%; The northern region, where Nam Dinh, Taiping and Hanoi are located, accounts for 40 percent.
It is reported that as of May 18, 2022, there are 2,787 foreign direct investment projects in Vietnam’s textile industry, with a total registered capital of $31.3 billion. According to Viet Nam Agreement 108/ND-CP of the Government, the textile industry is listed as an investment area for preferential treatment by the Government of Viet Nam
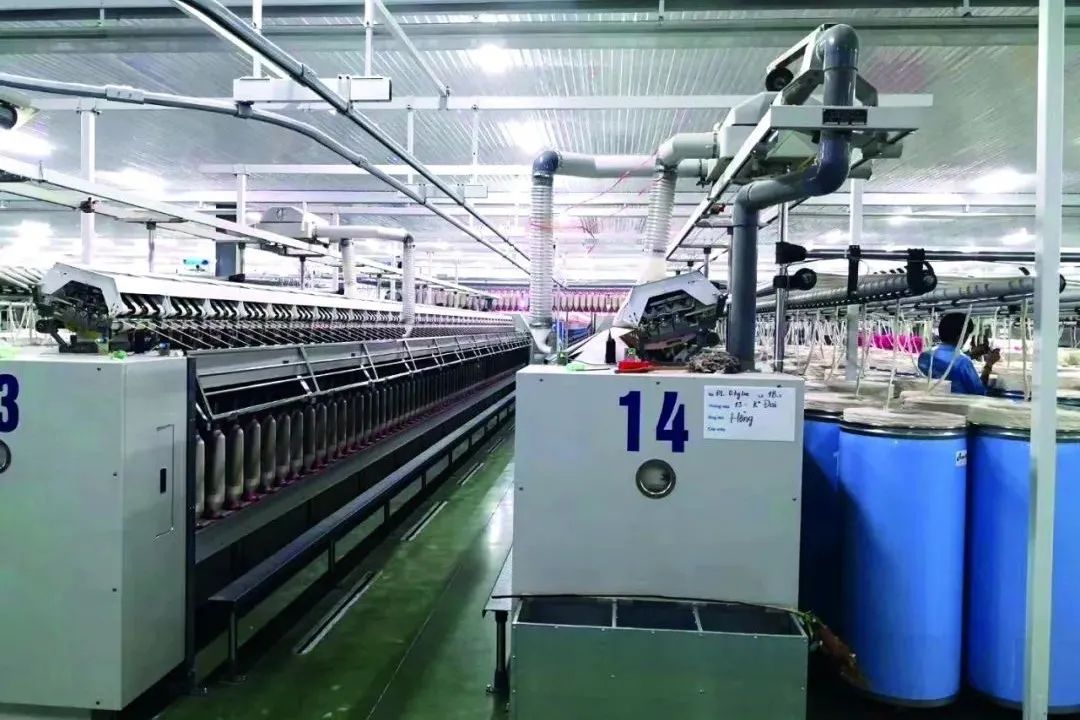
Textile Equipment Condition
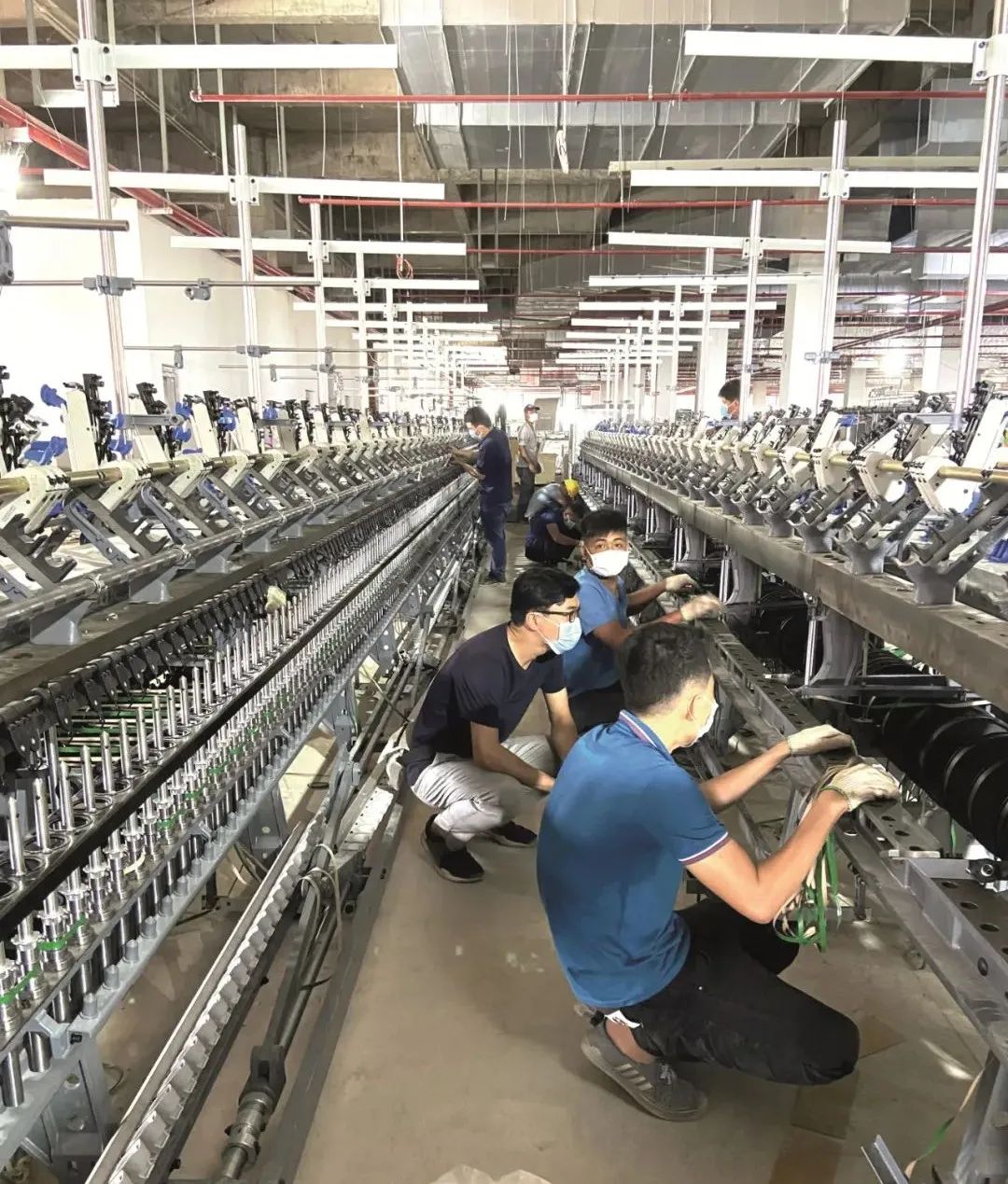
Driven by the “going global” of Chinese textile enterprises, Chinese equipment accounts for about 42% of Vietnam’s textile machinery market, while Japanese, Indian, Swiss and German equipment account for about 17%, 14%, 13% and 7%, respectively. With 70 percent of the country’s equipment in use and production efficiency low, the government is directing companies to automate existing equipment and encouraging investment in new spinning machines.
In the field of spinning equipment, Rida, Trutzschler, Toyota and other brands have been popular in the Vietnamese market. The reason why enterprises are keen to use them is that they can make up for the shortcomings in management and technology and ensure production efficiency. However, due to the high cost of equipment investment and long capital recovery cycle, general enterprises will only invest in individual workshops as a means to improve their corporate image and reflect their strength. Longwei products of India in recent years have also attracted more and more attention from local textile enterprises.
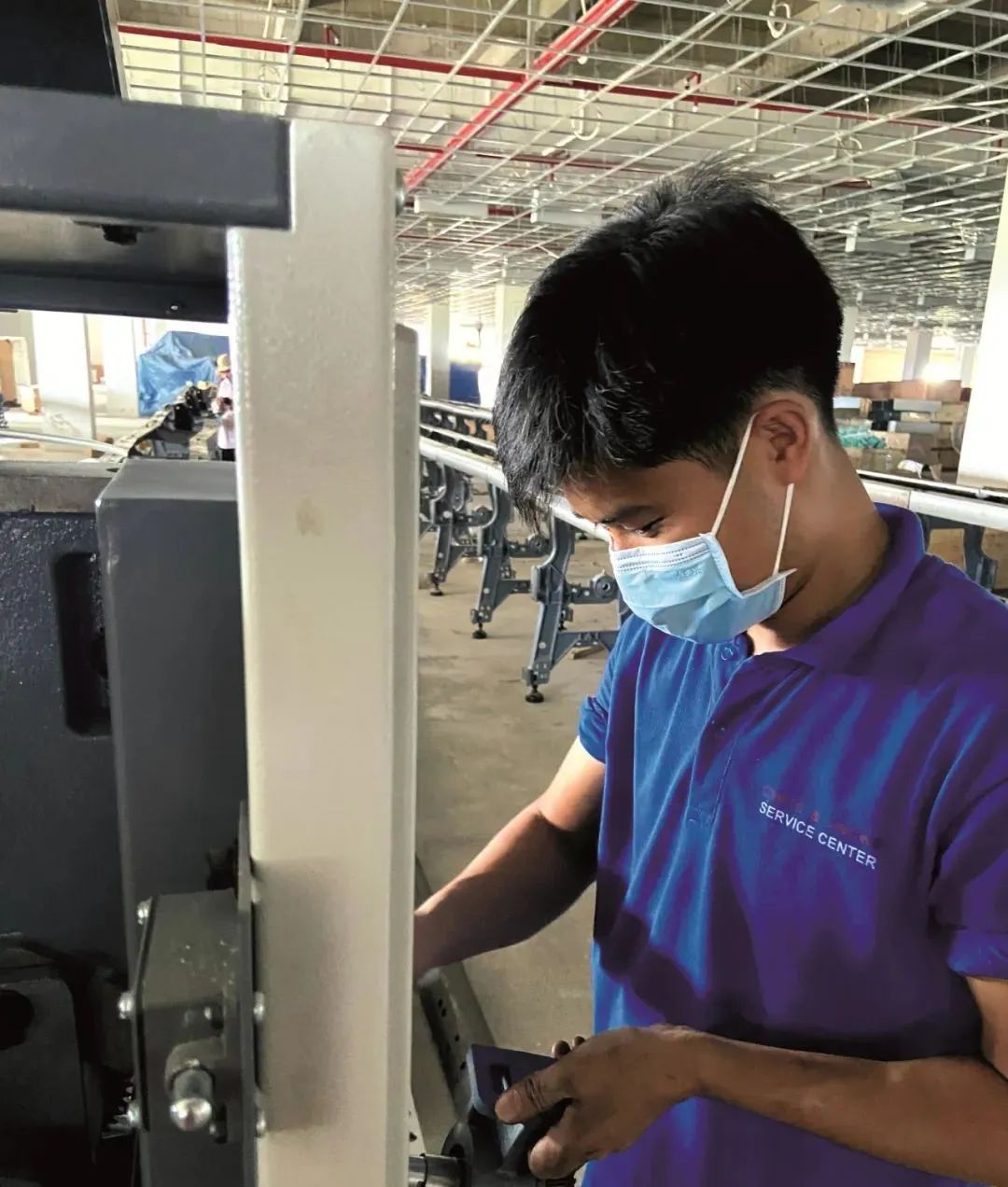
Chinese equipment has three advantages in the Vietnamese market: first, low equipment price, maintenance and maintenance cost; Second, the delivery cycle is short; Third, China and Vietnam have close cultural and trade exchanges, and many users are more interested in Chinese products. At the same time, China and Europe, Japan compared to the quality of equipment there is a certain gap, heavily dependent on installation and after-sales service, due to regional differences and service personnel quality level is uneven, affected the quality of service, left in the Vietnamese market “need frequent maintenance” impression.
Post time: Nov-21-2022